前端工程化速通版

前端工程化速通版
Huang_ChunES6
- ECMAScript(ES)是规范,JavaScript是ES的实现。
- ES6的第一个版本在2015年6月发布,正式名称《ECMAScript2015标准》(简称ES2015)
- ES6指的是5.1版本以后的JavaScript的下一代标椎,涵盖了ES2015.ES2016.ES2017等等。
let关键字
越域
推荐使用let关键字替代 var关键字声明变量,因为 var存在诸多问题,比如:
1 | { |
重复声明
1 | // var 可以声明多次 |
变量提升
1 | // var 会变量提升 |
const
1 | // 1. 声明之后不允许改变 |
解构
数组解构
1 | let arr = [1, 2, 3]; |
对象解构
1 | const person = { |
对象解构
1 | const person = { |
链判断
如果读取对象内部的某个属性,往往需要判断一下,属性的上层对象是否存在。
比如,读取message.body.user.firstName这个属性,安全的写法是写成下面这样。
1 | let message = null; |
这样的层层判断非常麻烦,因此 ES2020 引入了“链判断运算符”(optional chaining operator)?.,简化上面的写法。
1 | const firstName = message?.body?.user?.firstName || 'default'; |
参数默认值
1 | //在 ES6 以前,我们无法给一个函数参数设置默认值,只能采用变通写法: |
箭头函数
1 | //以前声明一个方法 |
1 | // 两个参数的情况: |
模板字符串
1 | let info = "你好,我的名字是:【"+name+"】,年龄是:【"+age+"】,邮箱是:【】" |
Promise
代表 异步对象,类似Java中的 CompletableFuture
Promise 是现代 JavaScript 中异步编程的基础,是一个由异步函数返回的可以向我们指示当前操作所处的状态的对象。在 Promise 返回给调用者的时候,操作往往还没有完成,但 Promise 对象可以让我们操作最终完成时对其进行处理(无论成功还是失败)
fetch 是浏览器支持从远程获取数据的一个函数,这个函数返回的就是 Promise 对象
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
"https://mdn.github.io/learning-area/javascript/apis/fetching-data/can-store/products.json"
);
console.log(fetchPromise);
fetchPromise.then((response) => {
console.log(`已收到响应:${response.status}`);
});
console.log("已发送请求……");
fetch api
fetch 是浏览器支持从远程获取数据的一个函数,这个函数返回的就是 Promise 对象
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
"https://mdn.github.io/learning-area/javascript/apis/fetching-data/can-store/products.json",
);
console.log(fetchPromise);
fetchPromise.then((response) => {
console.log(`已收到响应:${response.status}`);
});
console.log("已发送请求……");通过 fetch() API 得到一个 Response 对象;
● response.status: 读取响应状态码
● response.json():读取响应体json数据;(这也是个异步对象)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
"https://mdn.github.io/learning-area/javascript/apis/fetching-data/can-store/products.json",
);
fetchPromise.then((response) => {
const jsonPromise = response.json();
jsonPromise.then((json) => {
console.log(json[0].name);
});
});
Promise状态
首先,Promise 有三种状态:
● 待定(pending):初始状态,既没有被兑现,也没有被拒绝。这是调用 fetch() 返回 Promise 时的状态,此时请求还在进行中。
● 已兑现(fulfilled):意味着操作成功完成。当 Promise 完成时,它的 then() 处理函数被调用。
● 已拒绝(rejected):意味着操作失败。当一个 Promise 失败时,它的 catch() 处理函数被调用。
Promise对象
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// 执行异步操作
if (/* 异步操作成功 */) {
resolve(value);// 调用 resolve,代表 Promise 将返回成功的结果
} else {
reject(error);// 调用 reject,代表 Promise 会返回失败结果
}
});实例:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
$.ajax({
url: url,
type: "GET",
data: data,
success(result) {
resolve(result);
},
error(error) {
reject(error);
}
});
})
}
Async 函数
async function 声明创建一个绑定到给定名称的新异步函数。函数体内允许使用 await 关键字,这使得我们可以更简洁地编写基于 promise 的异步代码,并且避免了显式地配置 promise 链的需要。
● async 函数是使用async关键字声明的函数。async 函数是 AsyncFunction 构造函数的实例,并且其中允许使用 await 关键字。
● async 和 await 关键字让我们可以用一种更简洁的方式写出基于 Promise 的异步行为,而无需刻意地链式调用 promise。
● async 函数 返回的还是 Promise对象
2
3
4
// 这是一个异步函数
}在异步函数中,你可以在调用一个返回 Promise 的函数之前使用 await 关键字。这使得代码在该点上等待,直到 Promise 被完成,这时 Promise 的响应被当作返回值,或者被拒绝的响应被作为错误抛出。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
try {
// 在这一行之后,我们的函数将等待 `fetch()` 调用完成
// 调用 `fetch()` 将返回一个“响应”或抛出一个错误
const response = await fetch(
"https://mdn.github.io/learning-area/javascript/apis/fetching-data/can-store/products.json",
);
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`HTTP 请求错误:${response.status}`);
}
// 在这一行之后,我们的函数将等待 `response.json()` 的调用完成
// `response.json()` 调用将返回 JSON 对象或抛出一个错误
const json = await response.json();
console.log(json[0].name);
} catch (error) {
console.error(`无法获取产品列表:${error}`);
}
}
fetchProducts();
模块化
将 JavaScript 程序拆分为可按需导入的单独模块的机制。Node.js 已经提供这个能力很长时间了,还有很多的 JavaScript 库和框架已经开始了模块的使用(例如,CommonJS 和基于 AMD 的其他模块系统 如 RequireJS,以及最新的 Webpack 和 Babel)。
好消息是,最新的浏览器开始原生支持模块功能了。
工程架构
index.html
1 |
|
user.js
1 | const user = { |
npm
npm 是 nodejs 中进行 包管理 的工具;
下载:https://nodejs.org/en
环境
● 安装Node.js
● 配置 npm
2
npm config get registry #查看镜像源
命令
● npm init: 项目初始化;
○ npm init -y:默认一路yes,不用挨个输入信息
● npm install 包名:安装js包到项目中(仅当前项目有效)。指定 包名,或者 包名@版本号
○ npm install -g: 全局安装,所有都能用
○ 可以去 npm仓库 搜索第三方库
● npm update 包名:升级包到最新版本
● npm uninstall 包名:卸载包
● npm run:项目运行
使用流程
Java:
● 项目创建:Java环境 ==》 maven 初始化 ==》 添加依赖 ==》运行项目
● 项目迁移:Java环境 ==》 maven 下载依赖 ==》运行项目
Vite
简介
VITE
下一代的前端工具链
为开发提供极速响应
在GITHUB上查看
为什么选VITE?
VITECONF 23!
开始
●快速创建前端项目脚手架
●统一的工程化规范:目录结构、代码规范、git提交规范 等
●自动化构建和部署:前端脚手架可以自动进行代码打包、压缩、合并、编译等常见的构建工作,可以通过集成自动化部署脚本,自动将代码部署到测试、生产环境等;
实战
创建项目
1 | npm create vite #根据向导选择技术栈 |
安装依赖
1 | npm install #安装项目所有依赖 |
项目启动
1 | npm run dev #启动项目 |
项目部署
- 前后分离方式:需要把 dist 文件夹内容部署到如 nginx 之类的服务器上
- 前后不分离方式:把 dist 文件夹内容复制到 SpringBoot 项目 resources 下面
Vue3
我们使用 vite 创建 vue项目脚手架,并测试Vue功能
1 | npm create vite #根据向导选择技术栈 |
组件化
组件系统是一个抽象的概念;
● 组件:小型、独立、可复用的单元
● 组合:通过组件之间的组合、包含关系构建出一个完整应用
几乎任意类型的应用界面都可以抽象为一个组件树;
SFC
Vue 的单文件组件 (即 *.vue 文件,英文 Single-File Component,简称 SFC) 是一种特殊的文件格式,使我们能够将一个 Vue 组件的模板、逻辑与样式封装在单个文件中.
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
//编写脚本
</script>
<template>
//编写页面模板
</template>
<style scoped>
//编写样式
</style>
Vue工程
创建&运行
1 | npm create vite # 按照提示选择Vue |
运行原理
响应式 - ref()
数据的动态变化需要反馈到页面;
Vue通过ref()和reactive()包装数据,将会生成一个数据的代理对象。vue内部的 基于依赖追踪的响应式系统 就会追踪感知数据变化,并触发页面的重新渲染。
使用方式
使用步骤:
使用 ref() 包装原始类型、对象类型数据,生成 代理对象
任何方法、js代码中,使用 代理对象.value 的形式读取和修改值
页面组件中,直接使用 代理对象
注意:推荐使用 const(常量) 声明代理对象。代表代理对象不可变,但是内部值变化会被追踪。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
import { ref } from 'vue'
const count = ref(0)
function increment() {
count.value++
}
</script>
<template>
<button @click="increment">
{{ count }}
</button>
</template>深层响应性
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
const obj = ref({
nested: { count: 0 },
arr: ['foo', 'bar']
})
function mutateDeeply() {
// 以下都会按照期望工作
obj.value.nested.count++
obj.value.arr.push('baz')
}
响应式 - reactive()
使用步骤:
1 使用 reactive() 包装对象类型数据,生成 代理对象
2 任何方法、js代码中,使用 代理对象.属性的形式读取和修改值
3 页面组件中,直接使用 代理对象.属性
2
3
4
5
6
7
const state = reactive({ count: 0 })
<button @click="state.count++">
{{ state.count }}
</button>
计算属性 - computed
计算属性:根据已有数据计算出新数据
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
import {computed, reactive, toRef, toRefs} from "vue";
//省略基础代码
const totalPrice = computed(()=>{
return price.value * num.value - coupon.value*100
})
</script>
<template>
<div class="car">
<h2>优惠券:{{ car.coupon }} 张</h2>
<h2>数量:{{ car.num }}</h2>
<h2>单价:{{ car.price }}</h2>
<h1>总价:{{totalPrice}}</h1>
<button @click="getCoupon">获取优惠</button>
<button @click="addNum">加量</button>
<button @click="changePrice">加价</button>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
进阶用法
监听 - watch
1 | watch(num, (value, oldValue, onCleanup) => { |
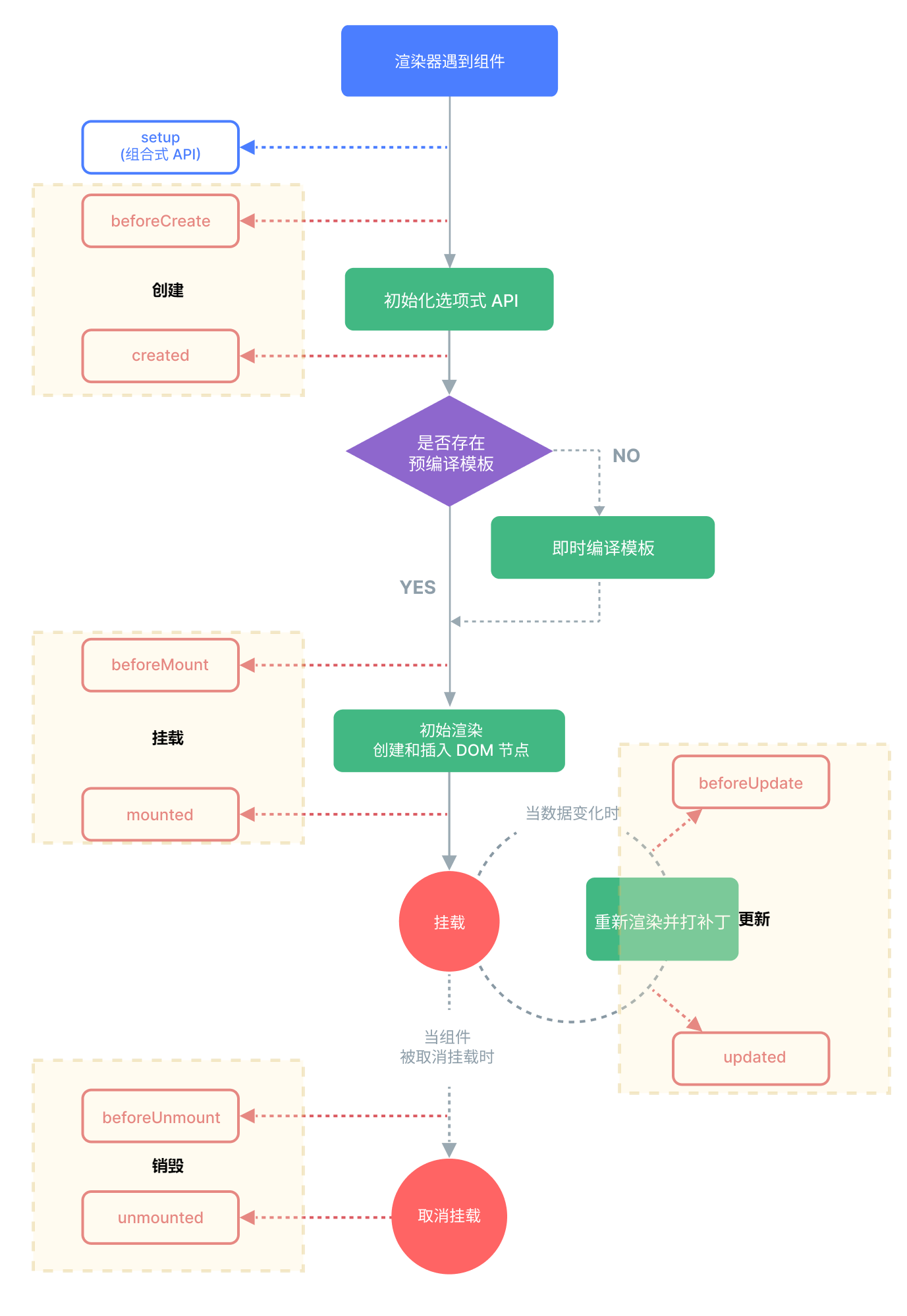
生命周期
每个 Vue 组件实例在创建时都需要经历一系列的初始化步骤,比如设置好数据侦听,编译模板,挂载实例到 DOM,以及在数据改变时更新 DOM。在此过程中,它也会运行被称为生命周期钩子的函数,让开发者有机会在特定阶段运行自己的代码。
生命周期整体分为四个阶段,分别是:创建、挂载、更新、销毁,每个阶段都有两个钩子,一前一后。
常用的钩子:
●onMounted(挂载完毕)
●onUpdated(更新完毕)
●onBeforeUnmount(卸载之前)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
import {onBeforeMount, onBeforeUpdate, onMounted, onUpdated, ref} from "vue";
const count = ref(0)
const btn01 = ref()
// 生命周期钩子
onBeforeMount(()=>{
console.log('挂载之前',count.value,document.getElementById("btn01"))
})
onMounted(()=>{
console.log('挂载完毕',count.value,document.getElementById("btn01"))
})
onBeforeUpdate(()=>{
console.log('更新之前',count.value,btn01.value.innerHTML)
})
onUpdated(()=>{
console.log('更新完毕',count.value,btn01.value.innerHTML)
})
</script>
<template>
<button ref="btn01" @click="count++"> {{count}} </button>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
组件传值
父传子 - Props
父组件给子组件传递值;
单向数据流效果:
● 父组件修改值,子组件发生变化
● 子组件修改值,父组件不会感知到
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
<Son :books="data.books" :money="data.money"/>
//子组件定义接受父组件的属性
let props = defineProps({
money: {
type: Number,
required: true,
default: 200
},
books: Array
});
子传父 - Emit
props 用来父传子,emit 用来子传父
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
let emits = defineEmits(['buy']);
function buy(){
// props.money -= 5;
emits('buy',-5);
}
//父组件感知事件和接受事件值
<Son :books="data.books" :money="data.money"
@buy="moneyMinis"/>
插槽 - Slots
子组件可以使用插槽接受模板内容。
基本使用
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
<button class="fancy-btn">
<slot></slot> <!-- 插槽出口 -->
</button>
<!-- 组件使用 -->
<FancyButton>
Click me! <!-- 插槽内容 -->
</FancyButton>默认内容
2
3
4
5
<slot>
Submit <!-- 默认内容 -->
</slot>
</button>具名插槽
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
<header>
<slot name="header"></slot>
</header>
<main>
<slot></slot>
</main>
<footer>
<slot name="footer"></slot>
</footer>
</div>使用: v-slot可以简写为 #
2
3
4
5
<template v-slot:header>
<!-- header 插槽的内容放这里 -->
</template>
</BaseLayout>
总结
路由
运行流程
路由配置
编写一个新的组件,测试路由功能;步骤如下:
- 编写 router/index.js文件
- 配置路由表信息
- 创建路由器并导出
- 在 main.js中使用路由
- 在页面使用router-link router-view完成路由功能
路径参数
使用 :变量名接受动态参数;这个成为 路径参数
2
3
4
5
6
// 匹配 /o/3549
{ path: '/o/:orderId' },
// 匹配 /p/books
{ path: '/p/:productName' },
]
嵌套路由
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
{
path: '/user/:id',
component: User,
children: [
{
// 当 /user/:id/profile 匹配成功
// UserProfile 将被渲染到 User 的 <router-view> 内部
path: 'profile',
component: UserProfile,
},
{
// 当 /user/:id/posts 匹配成功
// UserPosts 将被渲染到 User 的 <router-view> 内部
path: 'posts',
component: UserPosts,
},
],
},
]
编程式
useRoute:路由数据
路由传参跳转到指定页面后,页面需要取到传递过来的值,可以使用 useRoute方法;
拿到当前页路由数据;可以做
获取到当前路径
获取到组件名
获取到参数
获取到查询字符串
2
3
4
5
6
const route = useRoute()
// 打印query参数
console.log(route.query)
// 打印params参数
console.log(route.params)
useRouter:路由器
拿到路由器;可以控制跳转、回退等。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
const router = useRouter();
// 字符串路径
router.push('/users/eduardo')
// 带有路径的对象
router.push({ path: '/users/eduardo' })
// 命名的路由,并加上参数,让路由建立 url
router.push({ name: 'user', params: { username: 'eduardo' } })
// 带查询参数,结果是 /register?plan=private
router.push({ path: '/register', query: { plan: 'private' } })
// 带 hash,结果是 /about#team
router.push({ path: '/about', hash: '#team' })
//注意: `params` 不能与 `path` 一起使用
router.push({ path: '/user', params: { username } }) //错误用法 -> /user
路由传参
params参数
1 | <!-- 跳转并携带params参数(to的字符串写法) --> |
query参数
1 | <!-- 跳转并携带query参数(to的字符串写法) --> |
导航守卫
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
import HomeView from '../views/HomeView.vue'
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(import.meta.env.BASE_URL),
routes: [
{
path: '/',
name: 'home',
component: HomeView
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'about',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (About.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () => import('../views/AboutView.vue')
},
{
path: '/user/:name',
name: 'User',
component: () => import('@/views/user/UserInfo.vue'),
children: [
{
path: 'profile',
component: () => import('@/views/user/Profile.vue')
},
{
path: 'posts',
component: () => import('@/views/user/Posts.vue')
}
]
}
]
})
router.beforeEach(async (to, from) => {
console.log("守卫:to:", to)
console.log("守卫:from:", from)
if (to.fullPath === '/about') {
return "/"
}
})
export default router
总结
Axios
简介
Axios 是一个基于 promise 的网络请求库,可以用于浏览器和 node.js
2
3
axios.get('/user')
.then(res => console.log(resp.data))
请求
get请求
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
axios.get('/user?ID=12345')
.then(function (response) {
// 处理成功情况
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function (error) {
// 处理错误情况
console.log(error);
})
.finally(function () {
// 总是会执行
});携带请求参数
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
axios.get('/user', {
params: {
ID: 12345
}
})
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
})
.finally(function () {
// 总是会执行
});
post请求
默认post请求体中的数据将会以json方式提交
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
firstName: 'Fred',
lastName: 'Flintstone'
})
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
});
响应
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
// `data` 由服务器提供的响应
data: {},
// `status` 来自服务器响应的 HTTP 状态码
status: 200,
// `statusText` 来自服务器响应的 HTTP 状态信息
statusText: 'OK',
// `headers` 是服务器响应头
// 所有的 header 名称都是小写,而且可以使用方括号语法访问
// 例如: `response.headers['content-type']`
headers: {},
// `config` 是 `axios` 请求的配置信息
config: {},
// `request` 是生成此响应的请求
// 在node.js中它是最后一个ClientRequest实例 (in redirects),
// 在浏览器中则是 XMLHttpRequest 实例
request: {}
}
配置
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
baseURL: 'https://some-domain.com/api/',
timeout: 1000,
headers: {'X-Custom-Header': 'foobar'}
});
//可用的配置项如下:
{
// `url` 是用于请求的服务器 URL
url: '/user',
// `method` 是创建请求时使用的方法
method: 'get', // 默认值
// `baseURL` 将自动加在 `url` 前面,除非 `url` 是一个绝对 URL。
// 它可以通过设置一个 `baseURL` 便于为 axios 实例的方法传递相对 URL
baseURL: 'https://some-domain.com/api/',
// `transformRequest` 允许在向服务器发送前,修改请求数据
// 它只能用于 'PUT', 'POST' 和 'PATCH' 这几个请求方法
// 数组中最后一个函数必须返回一个字符串, 一个Buffer实例,ArrayBuffer,FormData,或 Stream
// 你可以修改请求头。
transformRequest: [function (data, headers) {
// 对发送的 data 进行任意转换处理
return data;
}],
// `transformResponse` 在传递给 then/catch 前,允许修改响应数据
transformResponse: [function (data) {
// 对接收的 data 进行任意转换处理
return data;
}],
// 自定义请求头
headers: {'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'},
// `params` 是与请求一起发送的 URL 参数
// 必须是一个简单对象或 URLSearchParams 对象
params: {
ID: 12345
},
// `paramsSerializer`是可选方法,主要用于序列化`params`
// (e.g. https://www.npmjs.com/package/qs, http://api.jquery.com/jquery.param/)
paramsSerializer: function (params) {
return Qs.stringify(params, {arrayFormat: 'brackets'})
},
// `data` 是作为请求体被发送的数据
// 仅适用 'PUT', 'POST', 'DELETE 和 'PATCH' 请求方法
// 在没有设置 `transformRequest` 时,则必须是以下类型之一:
// - string, plain object, ArrayBuffer, ArrayBufferView, URLSearchParams
// - 浏览器专属: FormData, File, Blob
// - Node 专属: Stream, Buffer
data: {
firstName: 'Fred'
},
// 发送请求体数据的可选语法
// 请求方式 post
// 只有 value 会被发送,key 则不会
data: 'Country=Brasil&City=Belo Horizonte',
// `timeout` 指定请求超时的毫秒数。
// 如果请求时间超过 `timeout` 的值,则请求会被中断
timeout: 1000, // 默认值是 `0` (永不超时)
// `withCredentials` 表示跨域请求时是否需要使用凭证
withCredentials: false, // default
// `adapter` 允许自定义处理请求,这使测试更加容易。
// 返回一个 promise 并提供一个有效的响应 (参见 lib/adapters/README.md)。
adapter: function (config) {
/* ... */
},
// `auth` HTTP Basic Auth
auth: {
username: 'janedoe',
password: 's00pers3cret'
},
// `responseType` 表示浏览器将要响应的数据类型
// 选项包括: 'arraybuffer', 'document', 'json', 'text', 'stream'
// 浏览器专属:'blob'
responseType: 'json', // 默认值
// `responseEncoding` 表示用于解码响应的编码 (Node.js 专属)
// 注意:忽略 `responseType` 的值为 'stream',或者是客户端请求
// Note: Ignored for `responseType` of 'stream' or client-side requests
responseEncoding: 'utf8', // 默认值
// `xsrfCookieName` 是 xsrf token 的值,被用作 cookie 的名称
xsrfCookieName: 'XSRF-TOKEN', // 默认值
// `xsrfHeaderName` 是带有 xsrf token 值的http 请求头名称
xsrfHeaderName: 'X-XSRF-TOKEN', // 默认值
// `onUploadProgress` 允许为上传处理进度事件
// 浏览器专属
onUploadProgress: function (progressEvent) {
// 处理原生进度事件
},
// `onDownloadProgress` 允许为下载处理进度事件
// 浏览器专属
onDownloadProgress: function (progressEvent) {
// 处理原生进度事件
},
// `maxContentLength` 定义了node.js中允许的HTTP响应内容的最大字节数
maxContentLength: 2000,
// `maxBodyLength`(仅Node)定义允许的http请求内容的最大字节数
maxBodyLength: 2000,
// `validateStatus` 定义了对于给定的 HTTP状态码是 resolve 还是 reject promise。
// 如果 `validateStatus` 返回 `true` (或者设置为 `null` 或 `undefined`),
// 则promise 将会 resolved,否则是 rejected。
validateStatus: function (status) {
return status >= 200 && status < 300; // 默认值
},
// `maxRedirects` 定义了在node.js中要遵循的最大重定向数。
// 如果设置为0,则不会进行重定向
maxRedirects: 5, // 默认值
// `socketPath` 定义了在node.js中使用的UNIX套接字。
// e.g. '/var/run/docker.sock' 发送请求到 docker 守护进程。
// 只能指定 `socketPath` 或 `proxy` 。
// 若都指定,这使用 `socketPath` 。
socketPath: null, // default
// `httpAgent` and `httpsAgent` define a custom agent to be used when performing http
// and https requests, respectively, in node.js. This allows options to be added like
// `keepAlive` that are not enabled by default.
httpAgent: new http.Agent({ keepAlive: true }),
httpsAgent: new https.Agent({ keepAlive: true }),
// `proxy` 定义了代理服务器的主机名,端口和协议。
// 您可以使用常规的`http_proxy` 和 `https_proxy` 环境变量。
// 使用 `false` 可以禁用代理功能,同时环境变量也会被忽略。
// `auth`表示应使用HTTP Basic auth连接到代理,并且提供凭据。
// 这将设置一个 `Proxy-Authorization` 请求头,它会覆盖 `headers` 中已存在的自定义 `Proxy-Authorization` 请求头。
// 如果代理服务器使用 HTTPS,则必须设置 protocol 为`https`
proxy: {
protocol: 'https',
host: '127.0.0.1',
port: 9000,
auth: {
username: 'mikeymike',
password: 'rapunz3l'
}
},
// see https://axios-http.com/zh/docs/cancellation
cancelToken: new CancelToken(function (cancel) {
}),
// `decompress` indicates whether or not the response body should be decompressed
// automatically. If set to `true` will also remove the 'content-encoding' header
// from the responses objects of all decompressed responses
// - Node only (XHR cannot turn off decompression)
decompress: true // 默认值
}
拦截器
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
axios.interceptors.request.use(function (config) {
// 在发送请求之前做些什么
return config;
}, function (error) {
// 对请求错误做些什么
return Promise.reject(error);
});
// 添加响应拦截器
axios.interceptors.response.use(function (response) {
// 2xx 范围内的状态码都会触发该函数。
// 对响应数据做点什么
return response;
}, function (error) {
// 超出 2xx 范围的状态码都会触发该函数。
// 对响应错误做点什么
return Promise.reject(error);
});
Pinia
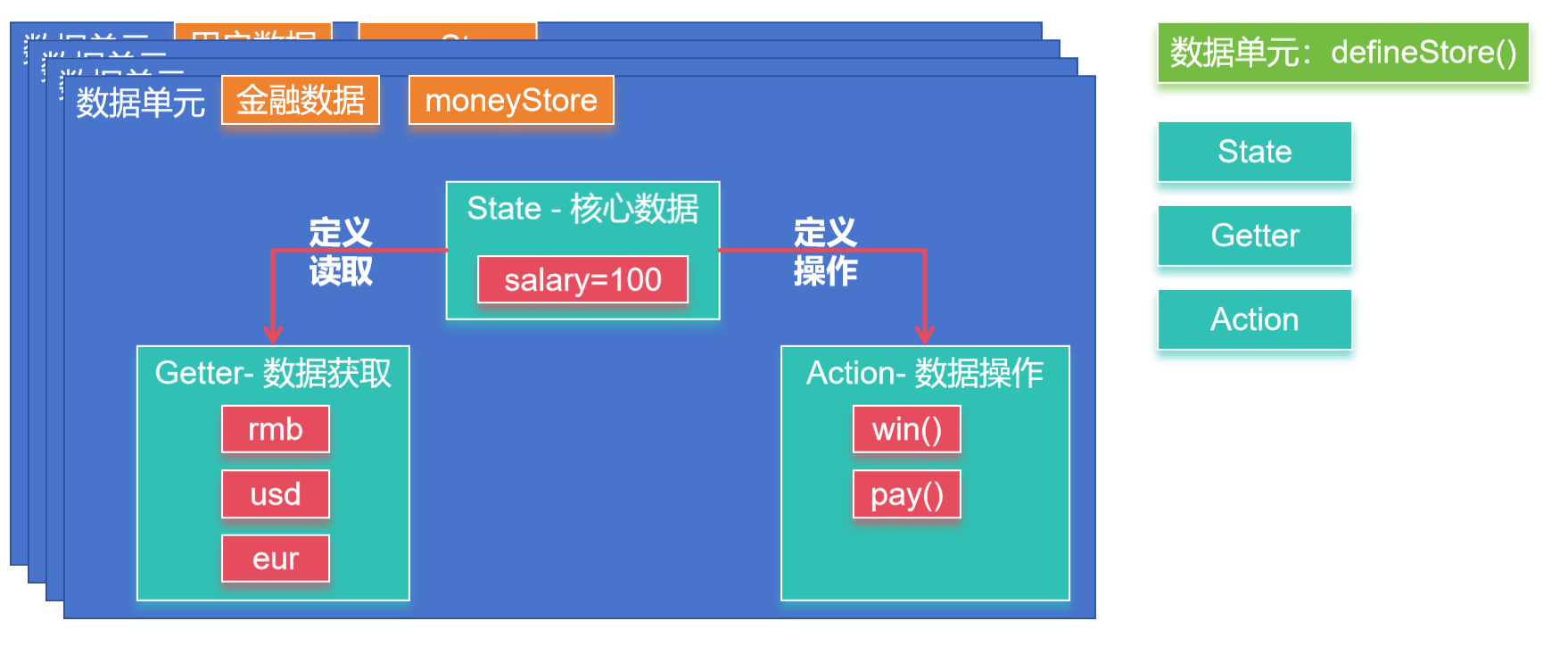
Pinia 是 Vue 的存储库,它允许您跨组件/页面共享状态。
Pinia 三个核心概念:
●State:表示 Pinia Store 内部保存的数据(data)
●Getter:可以认为是 Store 里面数据的计算属性(computed)
●Actions:是暴露修改数据的几种方式。
虽然外部也可以直接读写Pinia Store 中保存的data,但是我们建议使用Actions暴露的方法操作数据更加安全。
整合
main.js
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
import './style.css'
import App from './App.vue'
import {createPinia} from 'pinia'
const pinia = createPinia();
createApp(App)
.use(pinia)
.mount('#app')
案例
stores/money.js编写内容;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
//定义一个 money存储单元
export const useMoneyStore = defineStore('money', {
state: () => ({money: 100}),
getters: {
rmb: (state) => state.money,
usd: (state) => state.money * 0.14,
eur: (state) => state.money * 0.13,
},
actions: {
win(arg) {
this.money+=arg;
},
pay(arg){
this.money -= arg;
}
},
});App.vue
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
import Wallet from "./components/Wallet.vue";
import Game from "./components/Game.vue";
</script>
<template>
<Wallet></Wallet>
<Game/>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>Wallet.vue
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
import {useMoneyStore} from '../stores/money.js'
let moneyStore = useMoneyStore();
</script>
<template>
<div>
<h2>¥:{{moneyStore.rmb}}</h2>
<h2>$:{{moneyStore.usd}}</h2>
<h2>€:{{moneyStore.eur}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
div {
background-color: #f9f9f9;
}
</style>Game.vue
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
import {useMoneyStore} from '../stores/money.js'
let moneyStore = useMoneyStore();
function guaguale(){
moneyStore.win(100);
}
function bangbang(){
moneyStore.pay(5)
}
</script>
<template>
<button @click="guaguale">刮刮乐</button>
<button @click="bangbang">买棒棒糖</button>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
setup写法
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
const salary = ref(1000); // ref() 就是 state 属性
const dollar = computed(() => salary.value * 0.14); // computed() 就是 getters
const eur = computed(() => salary.value * 0.13); // computed() 就是 getters
//function() 就是 actions
const pay = () => {
salary.value -= 100;
}
const win = () => {
salary.value += 1000;
}
//重要:返回可用对象
return {salary,dollar,eur,pay,win}
})
脚手架
2
3
npm create vue@latest # 直接使用create-vue 创建项目
vue-cli #已经过时
Ant Design Vue
官网:https://www.antdv.com/
使用 npm create vue@latest 创建出项目脚手架,然后整合ant design vue安装依赖
全局注册: 编写main.js
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
import Antd from 'ant-design-vue';
import App from './App';
import 'ant-design-vue/dist/reset.css';
const app = createApp(App);
app.use(Antd).mount('#app');
布局
Layout:布局容器,其下可嵌套 Header Sider Content Footer 或 Layout 本身,可以放在任何父容器中。
○ Header:顶部布局,自带默认样式,其下可嵌套任何元素,只能放在 Layout 中。
○ Sider:侧边栏,自带默认样式及基本功能,其下可嵌套任何元素,只能放在 Layout 中。
○ Content:内容部分,自带默认样式,其下可嵌套任何元素,只能放在 Layout 中。
○ Footer:底部布局,自带默认样式,其下可嵌套任何元素,只能放在 Layout 中。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
<a-layout id="components-layout-demo" style="height: 100vh">
<a-layout-sider v-model:collapsed="collapsed" :trigger="null" collapsible>
<div class="logo" />
<a-menu v-model:selectedKeys="selectedKeys" theme="dark" mode="inline">
<a-menu-item key="1">
<user-outlined />
<span>nav 1</span>
</a-menu-item>
<a-menu-item key="2">
<video-camera-outlined />
<span>nav 2</span>
</a-menu-item>
<a-menu-item key="3">
<upload-outlined />
<span>nav 3</span>
</a-menu-item>
</a-menu>
</a-layout-sider>
<a-layout>
<a-layout-header style="background: #fff; padding: 0">
<menu-unfold-outlined
v-if="collapsed"
class="trigger"
@click="() => (collapsed = !collapsed)"
/>
<menu-fold-outlined v-else class="trigger" @click="() => (collapsed = !collapsed)" />
</a-layout-header>
<a-layout-content
:style="{ margin: '24px 16px', padding: '24px', background: '#fff', minHeight: '280px' }"
>
Content
</a-layout-content>
</a-layout>
</a-layout>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue';
const selectedKeys = ref(['1']);
const collapsed = ref(false);
</script>
<style>
#components-layout-demo .trigger {
font-size: 18px;
line-height: 64px;
padding: 0 24px;
cursor: pointer;
transition: color 0.3s;
}
#components-layout-demo .trigger:hover {
color: #1890ff;
}
#components-layout-demo .logo {
height: 32px;
background: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.3);
margin: 16px;
}
.site-layout .site-layout-background {
background: #fff;
}
</style>










.webp)





